Are SSD PCB compatible with all motherboard architectures?
When considering the purchase of a Solid State Drive, many users are concerned about the compatibility of the SSD PCB with various motherboard architectures. SSDs are now essential for fast data access and reliable storage, making it crucial for consumers to know whether the SSD they choose will integrate seamlessly into their existing system. The SSD PCB is vital in ensuring the drive functions correctly, but not all SSD PCBs are universally compatible with every motherboard architecture. This article will explore the factors influencing SSD PCB compatibility, including form factor, interface, and support for different motherboard types.
SSD PCB and Form Factor: A Key Factor in Compatibility
The form factor is one of the primary factors determining SSD PCB compatibility with motherboard architectures. An SSD’s form factor refers to the drive’s size and shape. Most consumer SSDs come in three common form factors: 2.5-inch, M.2, and PCIe. The 2.5-inch SSD, which typically uses the SATA interface, is widely compatible with most motherboards with a 2.5-inch drive bay.
However, M.2 SSDs and PCIe SSDs are smaller and may only fit into a motherboard’s available slots if the motherboard supports these specific form factors. M.2 drives, for example, come in various sizes (such as 2280 or 2230), which must match the slot provided on the motherboard. A motherboard that does not support M.2 connectors will be unable to accommodate an M.2 SSD PCB, no matter how advanced the drive’s technology. Therefore, when selecting an SSD, users must ensure that their motherboard supports the corresponding form factor of the SSD PCB.
Interface Compatibility: SATA, NVMe, and PCIe Protocols
Another essential factor is the interface through which the SSD connects to the motherboard. SATA (Serial ATA) and NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) are the two most common interface protocols SSDs use. SATA-based SSDs are compatible with most motherboards, as they use the standard SATA III interface that has been around for over a decade. However, NVMe SSDs, which offer significantly faster data transfer rates, require a motherboard with an M.2 slot that supports the PCIe interface.
PCIe SSDs, on the other hand, connect directly to the motherboard’s PCIe slots and provide extremely high read and write speeds. While both SATA and NVMe SSDs use PCBs for data handling, the key difference lies in the interface, which the motherboard must support. To ensure compatibility, users must verify whether their motherboard offers the necessary ports or slots for these interfaces.
NVMe SSD: Performance and Compatibility with Modern Motherboards
NVMe SSDs are a significant advancement over SATA SSDs, offering drastically improved performance thanks to the PCIe interface. The NVMe protocol allows for much faster data transfer speeds, making these drives highly attractive for users who demand high performance, such as gamers, content creators, and professionals working with large files. However, NVMe SSDs require specific motherboard architectures that support the PCIe lanes. These SSDs often come in the M.2 form factor and need a PCIe M.2 slot to be compatible.
While most modern motherboards, especially those designed for gaming and high-performance computing, come with at least one M.2 PCIe slot, older motherboards may lack this feature. Therefore, when upgrading or building a PC, users should ensure their motherboard supports NVMe drives to leverage the full potential of an NVMe SSD PCB.

SATA SSD: The Legacy Option for Wider Compatibility
Despite the rise of NVMe SSDs, SATA SSDs remain popular due to their compatibility with older motherboards. SATA SSD PCBs use the same SATA interface as traditional hard drives and can be installed in any motherboard with a SATA III connector. These SSDs offer excellent performance upgrades over conventional hard drives, especially in speed and durability. For users with older motherboards that do not support M.2 or PCIe, SATA SSDs are the go-to option. Although SATA SSDs do not match the lightning-fast speeds of NVMe SSDs, they significantly boost performance. They are an excellent option for users seeking reliable storage without the need to upgrade the motherboard. As such, SATA SSD PCBs are often more universally compatible with older and budget-friendly motherboards.
M.2 and PCIe Slots: Compatibility Issues and Limitations
While M.2 SSDs are becoming more common in modern systems, compatibility issues can arise based on the specific version of the M.2 slot supported by the motherboard. There are M.2 SATA and M.2 PCIe slots, with the latter being faster and more efficient. However, not all motherboards support both types of slots. For instance, some motherboards might only support M.2 SATA SSDs, meaning that buying an M.2 PCIe SSD will not be compatible with that motherboard. This is why checking the form factor and the interface support are essential when purchasing an SSD.
Moreover, even within the M.2 form factor, some motherboards only support specific sizes (e.g., 2280) of M.2 SSDs, further complicating the compatibility issue. Users should verify that the SSD PCB size matches their motherboard’s M.2 slot specifications.
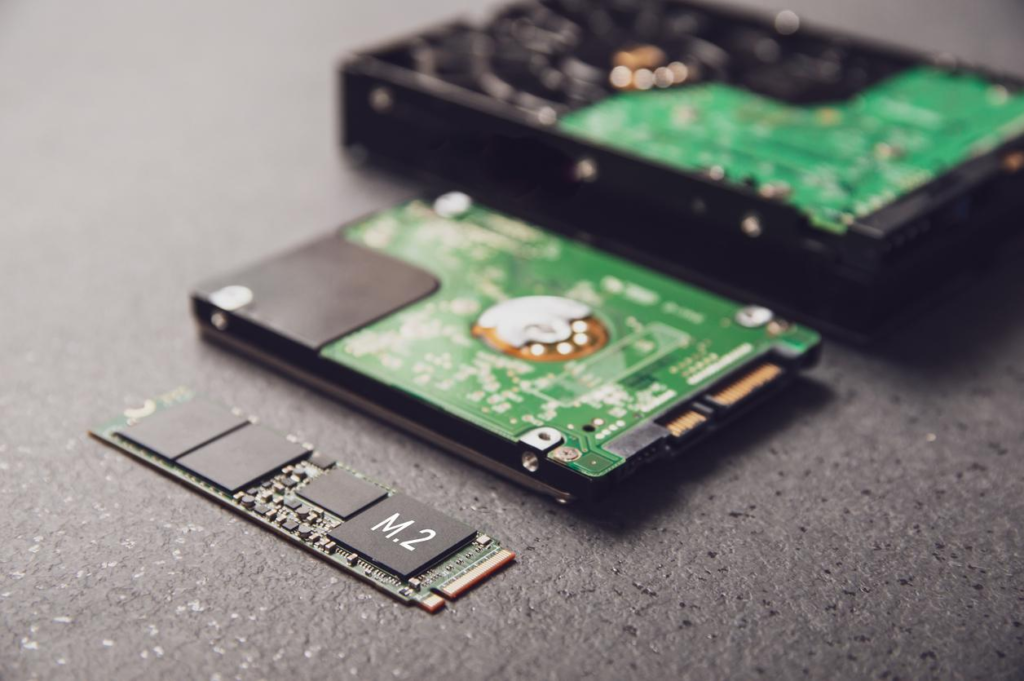

SSD PCB Features and Performance Across Different Architectures
Beyond form factor and interface, SSD PCBs also have different features that affect their compatibility and performance. Features such as DRAM cache and controller chipsets are essential in how the SSD performs within various motherboard architectures. For example, an SSD with a DRAM cache will provide better read and write speeds. However, not all motherboards can fully utilize this feature, depending on their architecture and performance capabilities. Additionally, the controller chip on the SSD PCB determines how well the SSD will communicate with the motherboard and handle heavy data loads. As such, users should consider the overall architecture of their system and ensure that it can support the SSD’s features. Matching the right SSD PCB with the right system is crucial to achieving optimal performance.
Ensuring Compatibility Between SSD PCB and Motherboard Architectures
While SSD PCBs offer significant performance advantages over traditional hard drives, compatibility with different motherboard architectures depends on various factors. These factors include the form factor, interface (SATA, NVMe, PCIe), and specific features such as data transfer speeds and controller chips. Modern motherboards generally support a wide range of SSD PCBs, but older systems may need to be compatible with newer NVMe or PCIe-based drives. Before purchasing an SSD, users must verify that their motherboard supports the desired form factor and interface, ensuring it will function optimally. Users can achieve impressive storage performance and system reliability with the right SSD PCB and a compatible motherboard.