NVMe vs. SATA SSD PCB: Which Truly Delivers the Best Performance?
Regarding storage solutions, the debate between NVMe and SATA SSDs is hot. Both technologies rely on SSD PCB to deliver performance but differ significantly in design, speed, and application. Understanding these differences is crucial for choosing the proper storage solution. This article dives deep into SSD PCB, comparing NVMe and SATA SSDs to determine which delivers the best performance.
Understanding SSD PCB: The Backbone of Storage Performance
The SSD PCB is the foundation of any solid-state drive, housing critical components like NAND flash memory, controllers, and connectors. Both NVMe and SATA SSDs rely on high-quality PCBs to ensure reliable data transfer and storage. However, the design and layout of these PCBs differ significantly between the two technologies.
For example, NVMe SSD PCBs are optimized for high-speed data transfer, often featuring multiple layers and advanced routing techniques. On the other hand, SATA SSD PCBs are designed for compatibility with older systems, prioritizing cost-effectiveness and simplicity. The quality of the SSD PCB directly impacts performance, making it a key factor in the NVMe vs SATA debate.
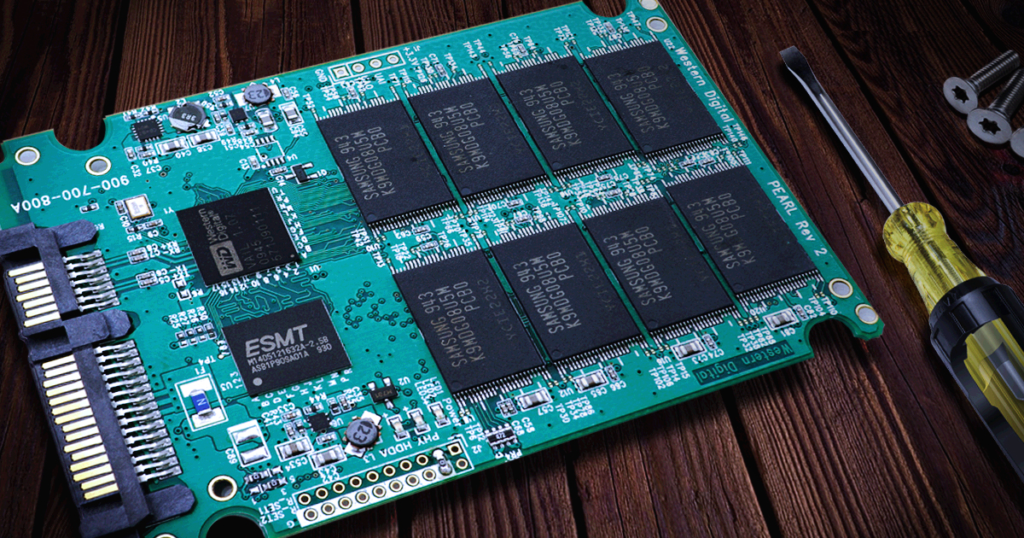
Speed and Bandwidth: NVMe’s Clear Advantage
Regarding speed, NVMe SSDs have a clear edge over SATA SSDs. NVMe SSD PCBs are designed to leverage the PCIe interface, offering significantly higher bandwidth than SATA. For instance, NVMe SSDs can achieve read/write speeds of up to 3,500 MB/s, while SATA SSDs are limited to around 550 MB/s.
This speed advantage is due to the advanced architecture of NVMe SSD PCBs, which support multiple data transfer lanes. In contrast, SATA SSD PCBs are restricted to a single lane, limiting their performance. If speed is your priority, NVMe is the clear winner. However, SATA SSDs remain viable for budget-conscious users or older systems.
Latency and Responsiveness: Why NVMe Excels
Latency is another area where NVMe SSDs outperform SATA SSDs. NVMe SSD PCBs are optimized for low latency, enabling faster access to stored data. This is particularly beneficial for tasks like gaming, video editing, and database management, where quick data retrieval is essential.
For example, NVMe SSDs typically have latency levels of just a few microseconds, compared to milliseconds for SATA SSDs. This difference is due to the streamlined communication protocol used by NVMe SSD PCBs, which reduces overhead and improves efficiency. If responsiveness is critical for your workload, NVMe is the better choice.

Compatibility and Ease of Use: SATA’s Strengths
While NVMe SSDs offer superior performance, SATA SSDs have the advantage of compatibility. SATA SSD PCBs are designed to work with older systems, making them a practical choice for legacy hardware users. Additionally, SATA SSDs are easier to install, using the same connectors as traditional hard drives.
For instance, upgrading a laptop or desktop with a SATA SSD is straightforward and doesn’t require special adapters or BIOS updates. This ease of use makes SATA SSDs attractive for casual users or those with limited technical expertise. If compatibility and simplicity are your priorities, SATA SSDs are the way to go.
Power Efficiency: NVMe’s Surprising Edge
Power efficiency is an often overlooked aspect of SSD performance. NVMe SSD PCBs are designed to minimize power consumption, making them ideal for laptops and other portable devices. For example, NVMe SSDs can enter low-power states when idle, reducing energy usage without sacrificing performance.
In contrast, SATA SSD PCBs are less efficient and rely on older power management techniques. This can lead to shorter battery life in laptops and higher energy costs for desktops. If power efficiency is a concern, NVMe SSDs offer a clear advantage.
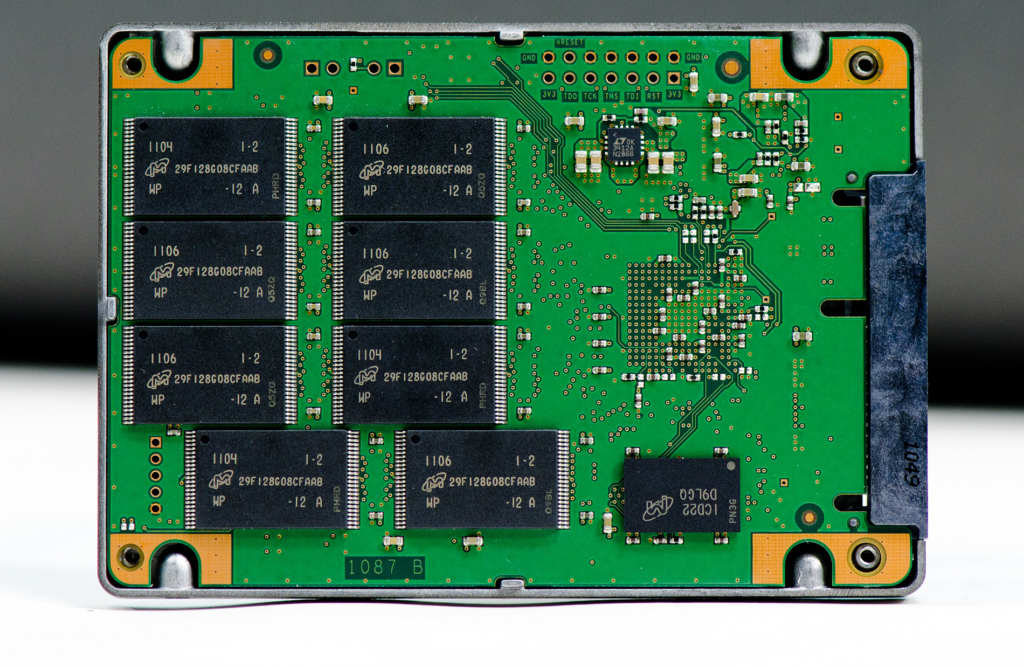
Cost and Value: SATA’s Budget-Friendly Appeal
Cost is a significant factor for many users, and SATA SSDs have a clear advantage in this area. SATA SSD PCBs are more straightforward and cheaper to produce, resulting in lower consumer prices. For example, a 1TB SATA SSD typically costs around 100, while a comparableNVMeSSDcancost100 and a comparableNVMeSSDcancost150 or more.
However, the price gap is narrowing as NVMe technology becomes more widespread. Additionally, the performance benefits of NVMe SSDs often justify the higher cost for power users. If budget is your primary concern, SATA SSDs offer excellent value for money.
Real-World Applications: Choosing the Right SSD PCB
The choice between NVMe and SATA SSDs depends on your specific needs. For gaming, content creation, or data-intensive tasks, NVMe SSD PCBs deliver the best performance. Their high speed and low latency make them ideal for demanding applications.
On the other hand, SATA SSD PCBs are better suited for general-purpose use, such as web browsing, office work, or upgrading older systems. They offer a balance of performance and affordability, making them a practical choice for casual users. Understanding your workload is key to choosing the correct SSD PCB.

The Future of SSD PCB: NVMe Leading the Way
The future of SSD PCBs is undoubtedly leaning toward NVMe technology. As PCIe 4.0 and 5.0 become more common, NVMe SSD PCBs will continue pushing the speed and efficiency boundaries. For example, PCIe 4.0 NVMe SSDs can achieve speeds of up to 7,000 MB/s, doubling the performance of previous generations.
SATA SSD PCBs, while still relevant, are becoming increasingly niche as NVMe technology dominates the market. According to a report by TrendForce, NVMe SSDs accounted for over 50% of the SSD market in 2023, and this share is expected to grow. If you’re investing in a new system, NVMe is the way to go.