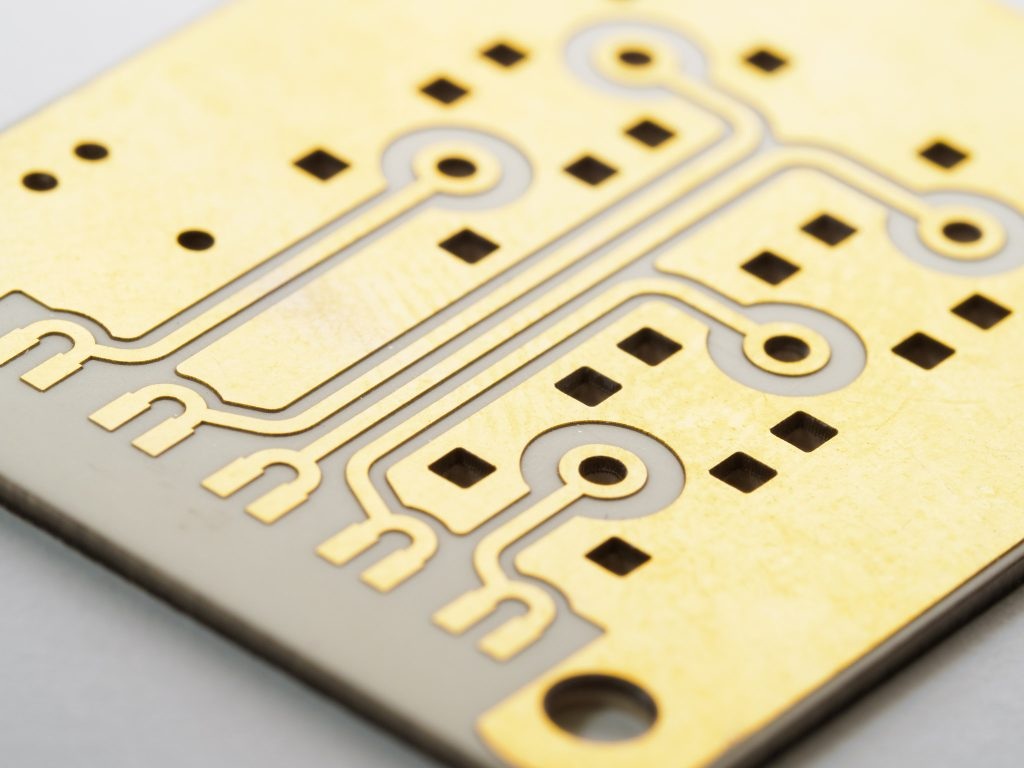
Due to their excellent performance characteristics, ceramic PCBs have become a significant choice for RF and microwave applications. While traditional PCB materials like FR4 have served well in many applications, RF and microwave systems require materials that can handle higher frequencies and temperatures. Ceramic PCB is emerging as the ideal solution. They offer unique benefits, […]
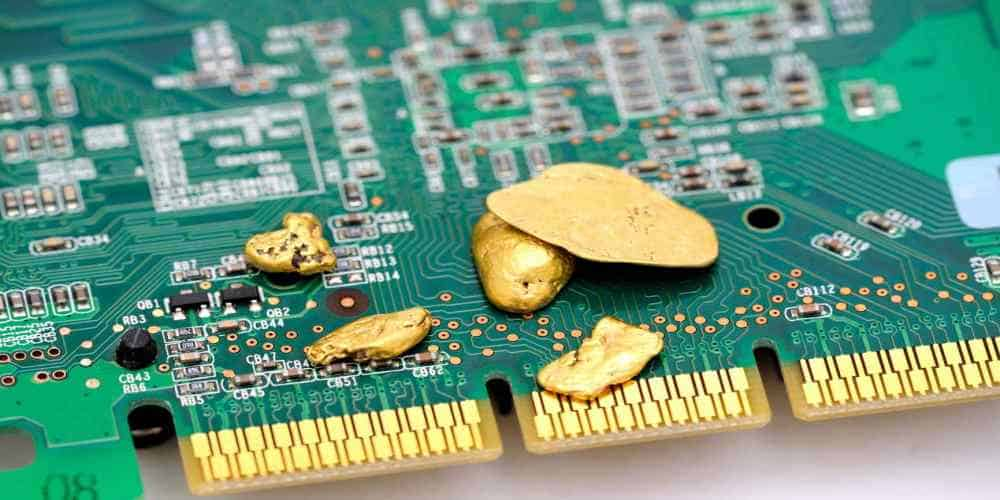
Gold finger PCBS are essential for high-speed and high-reliability electronic applications. In 2025, as edge connectors become more precise and demanding, beveling these gold fingers has grown from a niche process into a design standard. Why? Because poorly bevelled PCBS risk mechanical failure, connection instability, and costly replacements. Beveling creates a smooth, angled edge at […]
The SSD PCB is the heart of any solid-state drive, connecting all essential components that handle data storage and transmission. It houses the NAND flash memory, controller, power management ICs, DRAM (if present), and passive components that regulate the operation. Unlike mechanical drives, SSDs rely entirely on electronic components, which makes the PCB layout and […]
Designing Heavy Copper PCB demands precision beyond standard boards – optimizing thermal performance, current capacity, and structural integrity from the outset. While traditional PCB tools struggle with high-power requirements, modern interactive design platforms like Altium Designer and Cadence Allegro empower engineers to simulate thermal behaviour, adjust trace geometries, and validate current loads in real time. […]
In high-speed circuit design, electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk pose critical challenges that demand strategic PCB solutions. Double-sided PCBs provide engineers with essential tools to address these issues, offering dual-layer component placement and routing flexibility that significantly enhances signal integrity. By effectively separating analog and digital circuits across layers, these boards reduce noise coupling while […]
Over the past two decades, SSD PCB architecture has transformed storage technology. Starting with SATA-based designs that mimicked HDD limitations, it rapidly advanced to PCIe and NVMe interfaces that unlocked unprecedented speed and efficiency. This evolution didn’t just boost performance; it redefined how systems access data, powering everything from consumer laptops to enterprise servers. Today’s […]
Maintaining signal integrity is paramount for successful system performance in modern RF design. The Ceramic PCB has emerged as the substrate for high-frequency applications due to its exceptional dielectric properties and thermal characteristics. Unlike conventional FR-4 boards that struggle above a few GHz, ceramic substrates like alumina and aluminum nitride maintain stable electrical performance well […]
Gold Finger PCBs are vital for high-performance electronics, providing reliable connectivity in devices like graphics cards, RAM, and industrial equipment. The gold-plated edges offer excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, and durability. However, dust, moisture, and wear can affect their performance. Proper care and maintenance are key to extending the lifespan of your devices and avoiding costly […]
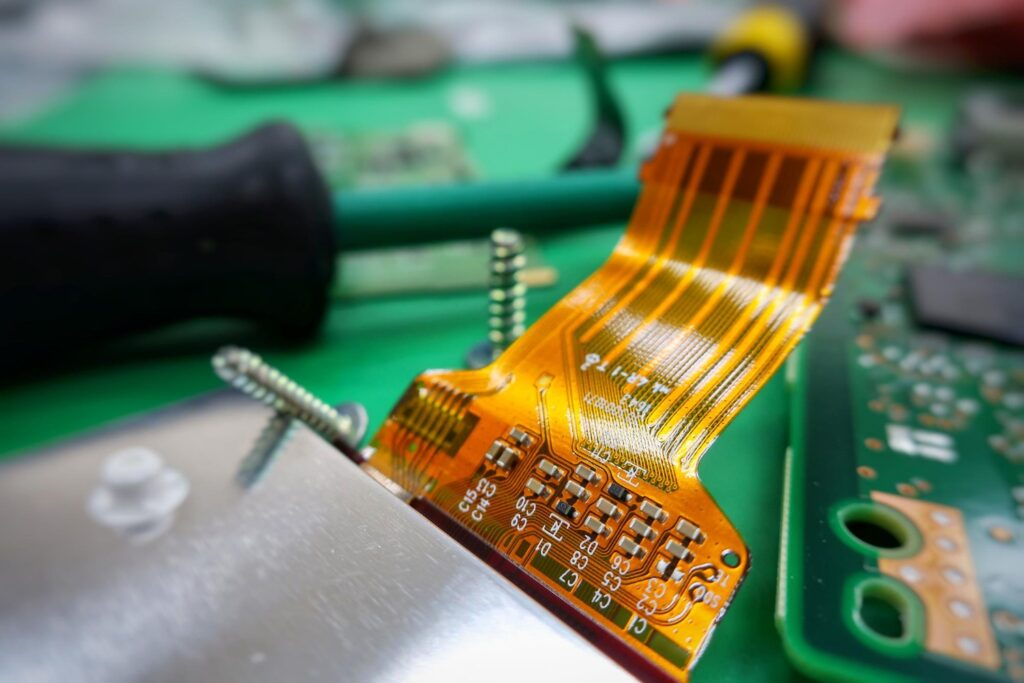
In industrial environments, durability and reliability are non-negotiable. Traditional PCBs often fall short under constant motion and stress. Rigid-Flex PCB technology combines rigid strength with flexible adaptability, offering a more innovative, resilient solution. Ideal for control systems, robotic arms, and high-vibration machinery, Rigid-Flex PCBs ensure performance where it matters most. In this blog post, we’ll […]
Carbon-ink PCB technology represents a cost-effective solution for various electronic applications. These printed circuit boards utilize conductive carbon-based inks instead of traditional copper traces, offering unique advantages in specific use cases. Due to their simplicity and reliability, carbon-ink PCB designs have gained popularity in consumer electronics, automotive controls, and medical devices. Carbon Ink PCB’s manufacturing process differs […]