A power converter can deliver hundreds of amps to a motor without overheating, warping, or failing due to vibration—the secret lies in its design: a suitable substrate, copper layer thickness, and mechanical dimensions. As a product manager at MZH Electronics, I’ve evaluated hundreds of high-current designs and guided clients in weighing the pros and cons […]
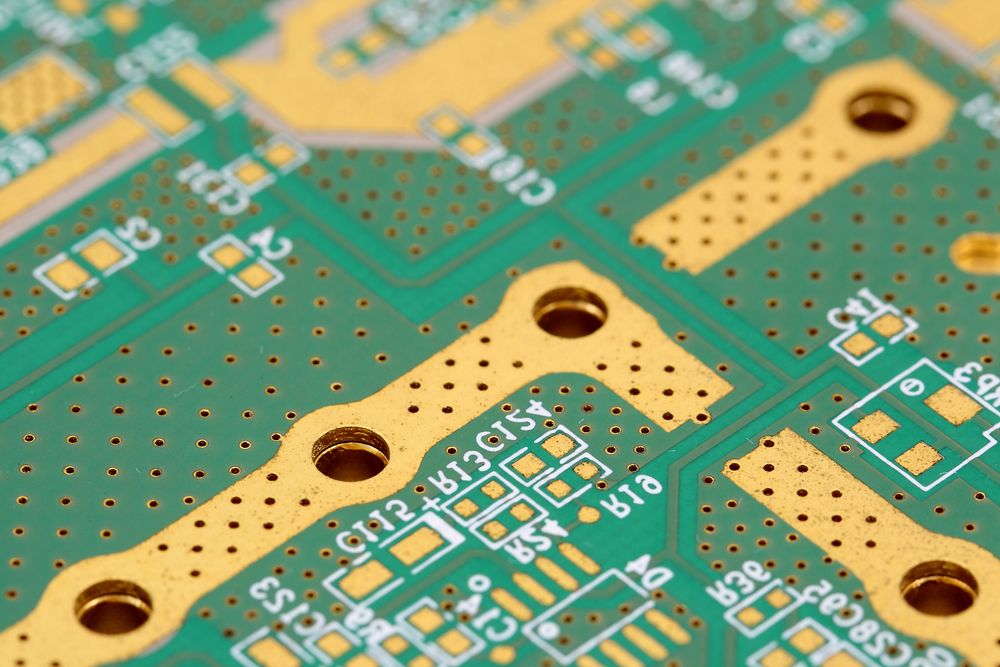
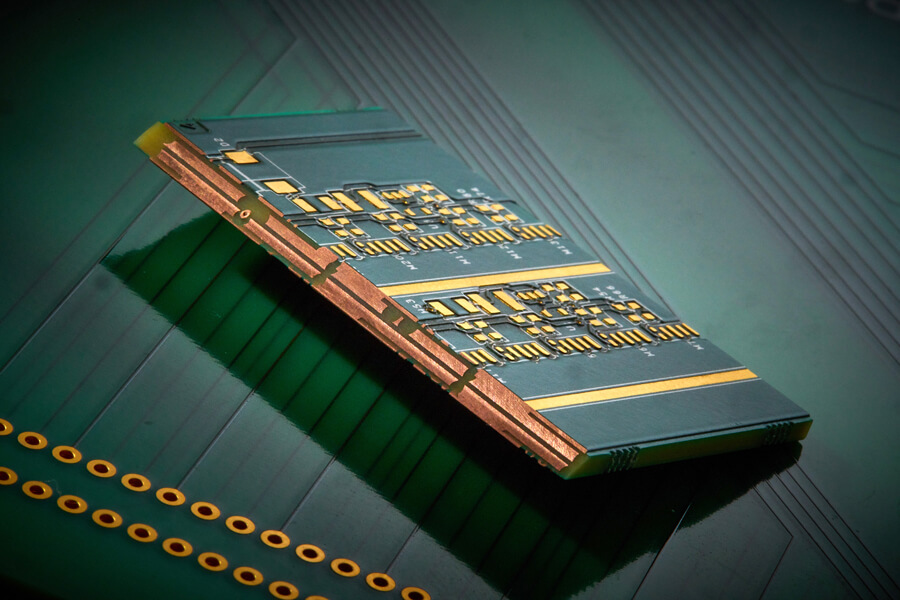
Thick copper PCB technology has become a critical pillar of Power Reliability Engineering as power systems are pushed harder than ever before. From EV fast-charging networks to industrial automation and renewable energy plants, modern electronics must deliver higher current, greater stability, and higher uptime in smaller, harsher environments. By combining heavy copper layers, optimized layouts, […]
thick copper PCB technology addresses one of the defining challenges in modern power electronics, where thermal control and performance gains go hand in hand. From electric vehicle charging stations to industrial motor drives and renewable energy inverters, higher power levels must now be delivered within increasingly compact designs. Thick copper PCBs play a critical role […]
Metal Base PCB, also known as a metal-core printed circuit board, is a critical technology that enables efficient heat dissipation and durable performance in harsh conditions. As a leading manufacturer and engineer of Metal Base PCB, we understand that our customers need both technical assurance and practical insights when evaluating Metal Base PCB systems for […]
Multilayer Ceramic PCB technology offers inherent thermal stability and low material expansion, unlike organic PCB materials. In a multilayer ceramic PCB, this stability extends across internal layers, ensuring consistent electrical pathways and predictable performance. For customers evaluating installation systems or long-term deployment, multilayer ceramic PCBs‘ reliability in extreme conditions is often the decisive factor, and […]
Thick Copper PCB and Heavy Copper Printed Circuit Board solutions are essential for power amplifier circuits that must handle high currents, dissipate heat efficiently, and endure mechanical stress. By offering enhanced electrical and thermal properties, thick copper PCBs ensure power amplifiers operate safely and efficiently under challenging conditions. High Current Capacity of Thick Copper PCB […]
Double sided FR4 PCB technology plays a vital role in electronics manufacturing because of its versatility and reliability. The choice of solder mask on double-sided FR4 PCBs directly affects its performance, durability, and manufacturability. Selecting the appropriate solder mask type enhances protection against environmental factors, improves assembly precision, and strengthens electrical insulation for these dual-layer FR4 […]
Custom SSD PCB solutions drive this evolution by tailoring PCB architecture to precise performance objectives. Rather than relying on generic layouts, engineers customise each to meet specific application needs. We specialise in the research, development, and manufacturing of Custom SSD PCBs, engineering every Solution to ensure stable, high-speed, and low-latency storage tailored to real-world operating […]
Driven by advancements in technology and the increasing demand for higher performance, efficiency, and miniaturization. At the heart of these innovations lies the Metal Substrate PCB, a key enabler for smarter, more reliable electronics. This specialized PCB technology is revolutionizing the way devices handle heat, electrical performance, and overall reliability. Heat Management in Modern Electronics […]
The Gold Finger PCB is indispensable in military electronics, providing the reliability, durability, and high performance that military systems require. Gold-finger PCBs, with their gold-plated connectors, withstand harsh environments while maintaining high performance. Military systems require components that can withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and corrosive environments, making gold finger PCBs an excellent solution. Military-Grade Gold […]