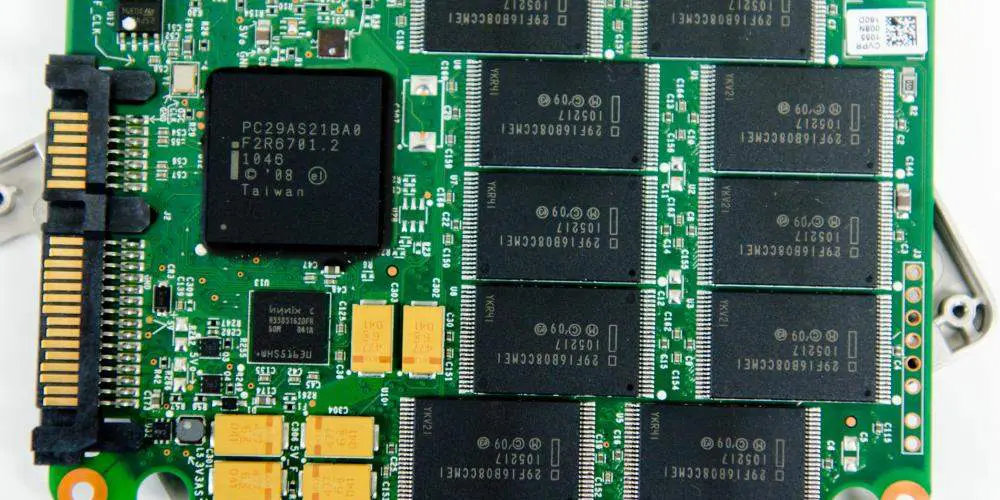
Can a 6-layer SSD PCB support high-density memory chips?
As data storage needs increase with modern applications, SSDs have emerged as a key solution. They offer high performance, speed, and reliability compared to traditional hard drives. At the core of an SSD lies the 6-layer SSD PCB, which plays a vital role in connecting and supporting various components, including memory chips. One of the most crucial questions when designing SSDs is whether a 6-layer SSD PCB can support high-density memory chips. High-density memory is increasingly vital as consumer demands for larger storage capacities and faster performance grow. In this article, we will explore how a 6-layer SSD PCB can facilitate the integration of high-density memory chips and enhance the overall performance of SSDs.
The Structure and Functionality of a 6-Layer PCB
To understand how a 6-layer SSD PCB supports high-density memory chips, it is essential first to grasp the structure and functionality of multi-layer PCBs. Typical 6-layer SSD PCBs consist of six layers of copper traces, insulating material, and electrical connections. These layers are strategically designed to ensure high-speed data transmission, signal integrity, and adequate power distribution.
In 6-layer SSD PCBs, the design uses the top and bottom layers for signal transmission, while the inner layers manage power and ground connections. The additional layers enable the PCB to carry more complex circuits and signals, making it an ideal candidate for high-density memory chips. By utilizing multiple layers, the 6-layer SSD PCBs can accommodate more components in a compact space, providing the flexibility needed for high-density configurations.
How High-Density Memory Chips Fit into a 6-Layer SSD PCB
High-density memory chips, such as NAND flash memory, are the heart of SSDs. These chips store vast amounts of data and enable quick access to information. The challenge with high-density memory is that it requires efficient signal routing and power management to function optimally.
The multi-layer design of a 6-layer SSD PCB effectively supports high-density memory chips. The inner layers can handle the increased number of connections needed for these memory chips, while the outer layers can focus on fast data transfer. Furthermore, the 6-layer SSD PCB design helps manage heat dissipation, which is critical for high-density memory chips that can generate substantial heat during operation.
By customizing the layout of the 6-layer SSD PCBs, manufacturers can ensure that high-density memory chips are appropriately integrated, offering optimal performance without compromising the SSD’s reliability or lifespan.
Signal Integrity and High-Speed Data Transmission
One of the main concerns when using high-density memory chips in SSDs is signal integrity. As memory density increases, so do the complexities of signal routing and noise management. In a 6-layer SSD PCB, careful design and optimized routing effectively address these challenges.
The use of multiple layers in a 6-layer SSD PCB allows for better signal integrity by reducing the distance between signal traces and ground layers. This reduces the likelihood of interference and cross-talk, which can degrade performance, especially when dealing with high-speed data transfer. High-density memory chips require fast and reliable communication to ensure that data is written and read at optimal speeds.
Moreover, the 6-layer SSD PCB can incorporate impedance-controlled traces, which are crucial for maintaining the integrity of high-speed signals. This ensures that the SSD performs efficiently even with high-density memory chips that require rapid data access.
Thermal Management in High-Density Memory Configurations
Due to the increased number of cells and more complex processing, high-density memory chips often generate more heat. Without proper thermal management, overheating can lead to performance degradation or even permanent damage to the components. A 6-layer SSD PCB offers a significant advantage in this regard by effectively managing heat dissipation.
The design of a 6-layer SSD PCB allows for better thermal distribution. By utilizing the inner layers for power and ground connections, heat can be spread more evenly throughout the board, reducing the risk of hot spots. Additionally, some 6-layer SSD PCBs can incorporate thermal vias, which are conductive paths that transfer heat from the surface of the PCB to the inner layers. This ensures that high-density memory chips remain within a safe operating temperature range, contributing to the SSD’s overall longevity.
Power Distribution and Grounding for High-Density Memory
Power distribution is another critical factor when designing 6-layer SSD PCBs that support high-density memory chips. As the memory density increases, so does the demand for power. Efficient power distribution ensures that each memory chip receives the necessary voltage while preventing power fluctuations that could negatively affect performance.
In a 6-layer SSD PCB, the inner layers are dedicated to power and ground planes, which help stabilize the power supply and provide a low-resistance path for the current. This setup is essential for high-density memory configurations, as it reduces noise and ensures that the memory chips receive clean and stable power. Additionally, grounding layers in the PCB help prevent electrical interference, which could compromise the performance of high-density memory chips.
A 6-layer SSD PCB optimizes power distribution and grounding to ensure that high-density memory chips operate efficiently, enabling faster data read/write speeds and greater storage capacity.
Advantages of Using a 6-Layer PCB for High-Density Memory in SSD
There are several advantages to using a 6-layer SSD PCB for high-density memory configurations. The multi-layer design provides more space for routing complex circuits, allowing for the integration of high-density memory chips without increasing the size of the SSD. This is crucial in the competitive SSD market, where smaller, more powerful storage devices are in high demand.
Additionally, the 6-layer SSD PCB enhances performance by improving signal integrity, reducing electromagnetic interference, and optimizing power distribution. These factors are essential when working with high-density memory chips, which require stable and high-speed communication to function optimally.
Furthermore, the 6-layer SSD PCB allows for better thermal management, ensuring that the memory chips stay calm and perform efficiently even under heavy workloads. This contributes to the SSD’s overall reliability and longevity, making it a valuable solution for high-performance applications.
The Future of High-Density Memory and SSD PCB
As the demand for higher storage capacities and faster data speeds continues to grow, the future of high-density memory in SSDs looks promising. Advances in NAND flash technology are constantly pushing the boundaries of memory density, and 6-layer SSD PCBs are well-positioned to support these innovations.
In the future, we may see even higher-density memory chips integrated into 6-layer SSD PCBs, further enhancing storage capabilities while maintaining high performance. Additionally, the continued development of power-efficient designs and thermal management solutions will ensure that SSDs equipped with high-density memory continue to operate reliably.
As technology evolves, the role of 6-layer SSD PCBs in supporting high-density memory will become even more critical, enabling the next generation of SSDs to meet the growing demands of consumers and industries alike.
The Viability of 6-Layer PCBs for High-Density Memory SSDs
A 6-layer SSD PCB can undoubtedly support high-density memory chips, providing the necessary infrastructure for efficient data transfer, power distribution, and heat management. By utilizing the advantages of a multi-layer design, 6-layer SSD PCBs offer the flexibility and reliability needed to integrate high-density memory without compromising performance. For manufacturers and users seeking high-performance SSDs with large storage capacities, a 6-layer SSD PCB is an excellent choice. It ensures optimal functionality and long-term reliability, making it a vital component in the evolution of storage technology.

