Materials Choice by PCB Manufacturer: Understanding Substrate Options
For PCB manufacturing, the choice of substrate material will largely affect the performance and reliability of the product. PCB manufacturer will select substrate materials based on the application’s requirements, considering factors such as thermal conductivity, dielectric constant, mechanical strength, and cost. This article will explore the various substrate options available to PCB manufacturers.
Type of substrate material selected by PCB manufacturer
FR-4: is a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate that consists of a braided layer of fiberglass impregnated with epoxy resin, then compressed and cured under heat and pressure to form a strong, rigid substrate with excellent electrical insulation properties, mechanical strength, and dimensional stability. One of the main advantages of FR-4 is its excellent electrical properties, including high dielectric strength, low loss tangent, and good insulation resistance.
FR-2: FR-2, also known as phenolic paper or phenolic cotton, is a laminated material composed of paper or cotton fabric impregnated with phenolic resin. One of its key features is its affordability. Using paper or cotton as the base material makes FR-2 a cost-effective choice for applications where budget constraints are a major consideration. Provides good electrical insulation but has lower mechanical strength than FR-4.
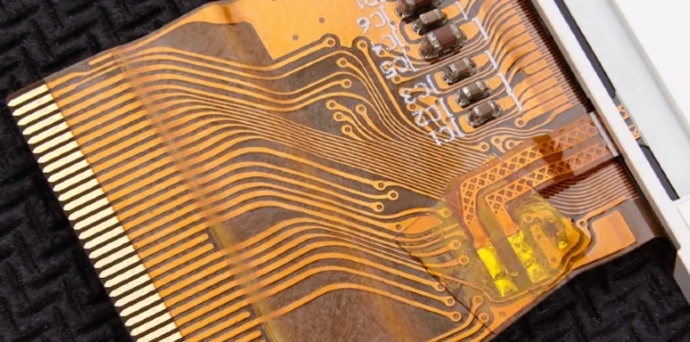
Polyimide: Polyimide, is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent thermal resistance and chemical inertness. It can withstand extreme temperatures from -269°C to over 400°C without significant degradation, making it ideal for applications exposed to both high and low temperatures.
Metal Core: Typically made of aluminum, copper, or a combination of metals, sandwiched between a layer of dielectric material and copper traces. The metal core acts as an effective heat sink, dissipating heat generated by components mounted on the PCB to improve thermal performance and reliability. People commonly use it in high-power LED lighting, automotive electronics, power electronics, and other applications where thermal management is critical.

Considerations for substrate selection
There are also some key factors that PCB manufacturers consider when selecting substrate materials. The substrate must have good electrical insulation properties to prevent short circuits and ensure signal integrity. The substrate material should also provide sufficient mechanical strength and stiffness to support components and withstand handling, assembly, and environmental stresses without deformation or damage. It must also be compatible with PCB manufacturing processes, including etching, plating, soldering, and cleaning. Dimensional stability is also important to maintain the accuracy of PCB features and ensure proper alignment during manufacturing processes such as drilling, etching, and soldering.
Choose the right substrate!
Proper substrate material selection is a critical decision in PCB manufacturing and can significantly impact the final product’s performance, reliability, and cost. Therefore, it is important for PCB manufacturers to carefully evaluate electrical, thermal, mechanical, and cost considerations when selecting a substrate material for a specific application to ensure a successful PCB design.

